NEWYou can now listen to Fox News articles!
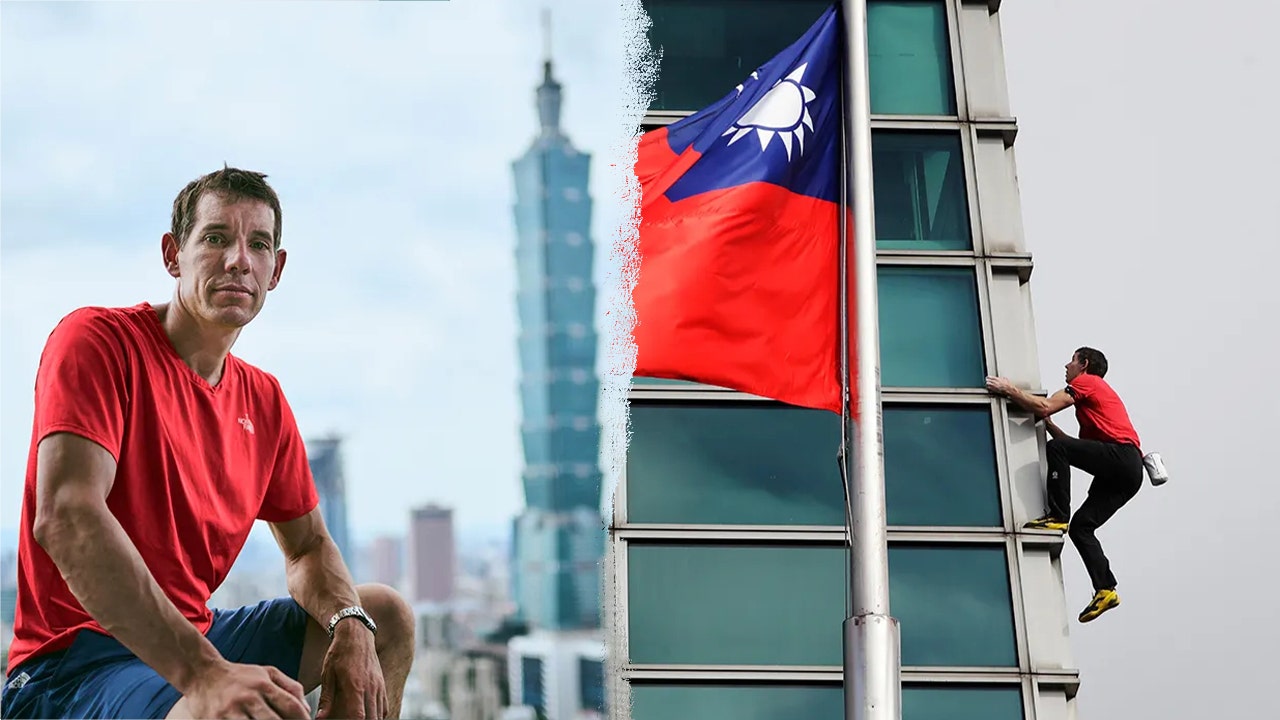
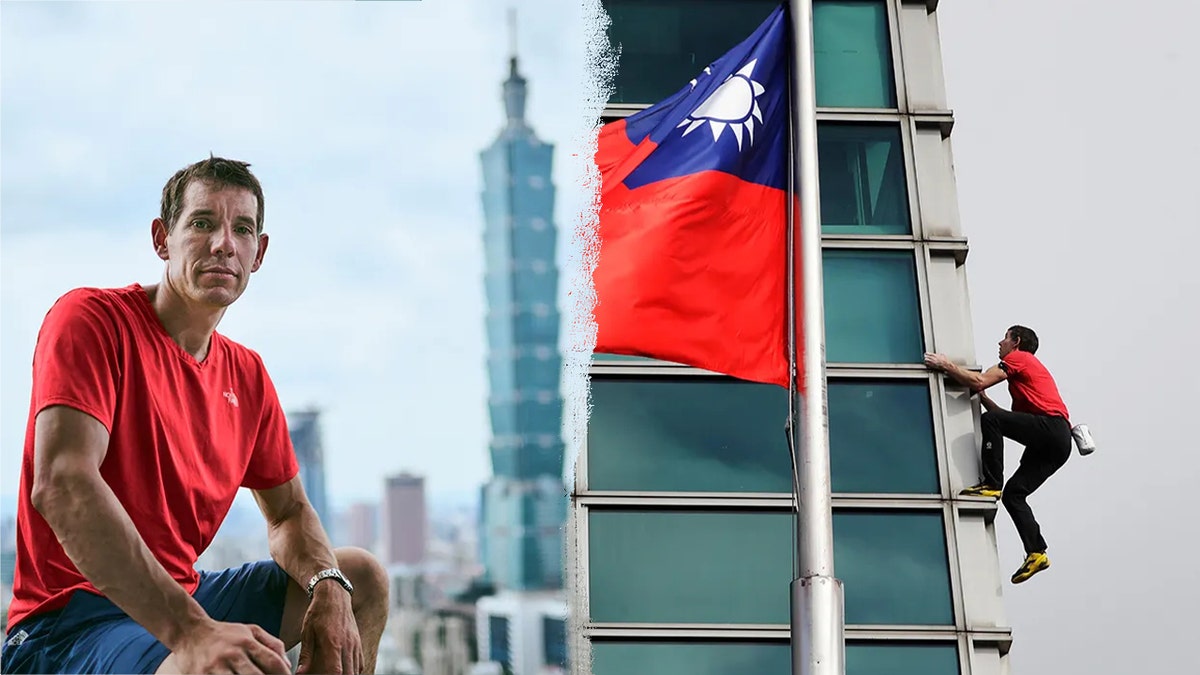
U.S. professional rock climber Alex Honnold upped the ante during his recent urban climb in Taiwan.
The daredevil athlete scaled the Taipei 101 skyscraper on Jan. 25 with no ropes or protective equipment. The event was streamed live on Netflix, as Fox News Digital previously reported.
Honnold successfully reached the summit of the 101-story steel building in just an hour and 31 minutes, waving his arms in victory at the top. He later noted the view was “amazing,” even though it was windy.
ONE MAN TURNED A GLOBAL SKYSCRAPER INTO HIS MOST DANGEROUS DESTINATION OF ALL: ‘PRETTY SURREAL’
As a career climber, Honnold’s conquests have included major mountain ranges across the U.S., plus Greenland’s massive sea cliffs — three times the size of the Empire State Building.
In a 2016 experiment, neuroscientist Jane Joseph set out to discover what in Honnold’s brain possessed him to take on such scary climbing by scanning it.
The doctor was one of the first to perform fMRI scans — functional magnetic resonance imaging — on “high sensation seekers,” according to a Nautilus report.
Joseph and a team of technicians found that Honnold’s amygdala showed little activity in reaction to images that would typically trigger fear and stress reactions.
“Nowhere in the fear center of Honnold’s brain could the neuroscientist spot activity,” the report noted.
PSYCHIATRIST REVEALS HOW SIMPLE MINDSET SHIFTS CAN SIGNIFICANTLY REDUCE CHRONIC PAIN
The researchers flipped the experiment, introducing a reward task where Honnold could win money. Normally, a control subject’s amygdala and other brain structures “look like a Christmas tree lit up,” Joseph said.
But Honnold’s was “lifeless in black and white.” Activity showed only in the regions that process visual input — confirming that he was awake and looking at the screen.

“There’s just not much going on in my brain,” Honnold told Joseph. “It just doesn’t do anything.”
Dr. Daniel Amen, the founder of Amen Clinics and a California-based psychiatrist, did not scan Honnold’s brain but is an expert in brain imaging.
In the brain scans of other extreme athletes and adrenaline junkies, Amen said there’s often lower baseline activity in the prefrontal cortex, which is involved in fear inhibition, impulse control and risk evaluation.
“Their brains are less easily ‘scared’ and more strongly driven by challenge and novelty.”
In these individuals, there is also a strong activation of reward and motivation circuits, or dopamine pathways, according to Amen.
CLICK HERE TO DOWNLOAD THE FOX NEWS APP
“Meaning, high stimulation feels normal — or even necessary — for them to feel engaged,” he said. “Some also show reduced reactivity in the amygdala, so situations that trigger fear in most people don’t produce the same alarm response.”
He added, “In short, their brains are less easily ‘scared’ and more strongly driven by challenge and novelty.”
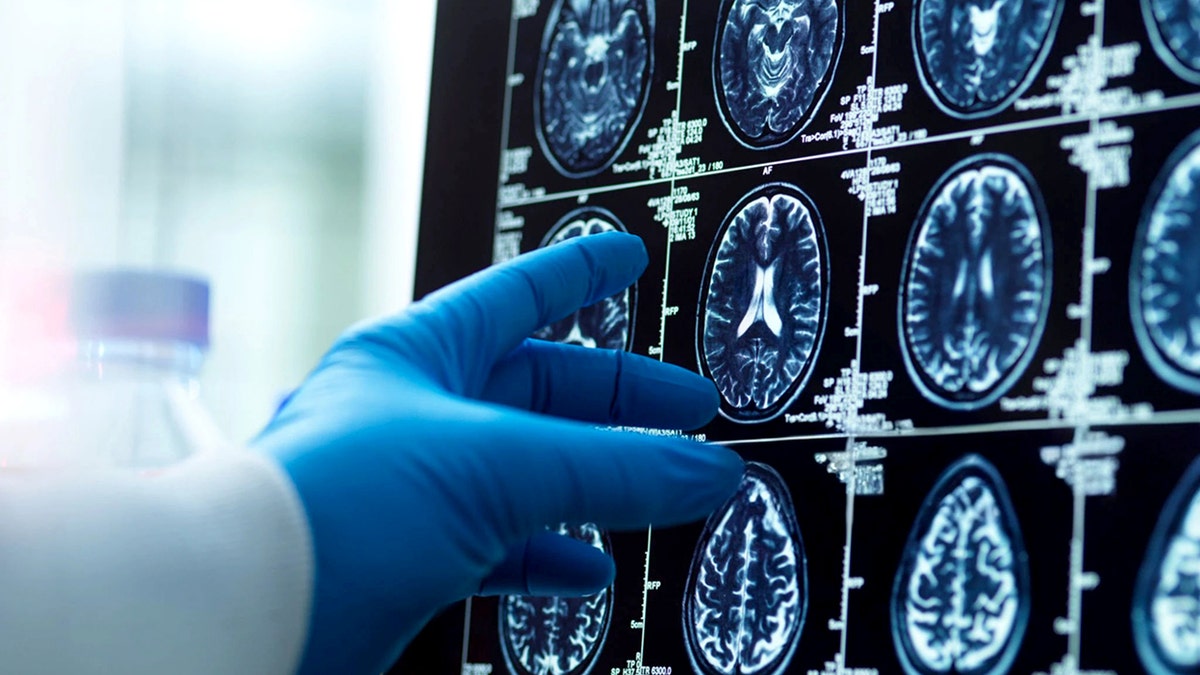
Based on nearly 300,000 brain scans done at Amen Clinics, Dr. Amen noted that in people like Honnold who are “elite extreme performers,” the key difference compared to the average brain is “exceptional top-down control.”
CLICK HERE FOR MORE HEALTH STORIES
“The prefrontal cortex stays online and organized under stress, allowing precise focus, emotional regulation and decision-making in high-risk environments,” he said. “Fear circuits activate just enough to sharpen attention — but not enough to overwhelm performance.”
CLICK HERE TO SIGN UP FOR OUR HEALTH NEWSLETTER
Brains like Honnold’s are also often “very efficient” in sensory-motor integration, or when vision, balance and motor planning “work seamlessly together.”
“Instead of panic, the brain enters a highly regulated, flow-state pattern where attention is narrow, calm and precise,” he said.
In the average brain, fear circuits tend to activate faster and louder, according to Amen — and the prefrontal cortex “tends to go offline” under threat, triggering hesitation, overthinking or panic.
“Most people experience a strong mismatch between perceived risk and control, which is protective for survival but limits extreme performance,” he said.
TEST YOURSELF WITH OUR LATEST LIFESTYLE QUIZ
“For the average person, high adrenaline disrupts accuracy and judgment; for extreme athletes, it organizes the brain,” he said.
“Their brains are not reckless — they are better regulated under stress, whereas the average brain prioritizes safety and avoidance.”
Fox News Digital’s Jessica Mekles contributed reporting.


